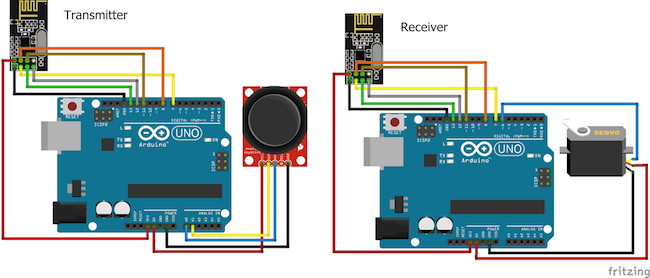
Control a servo motor with a joystick module by creating a transmitter and receiver with Arduinos and NRF24L01 modules!
HARDWARE
TOOLS
| 1 | Connecting wires | ||
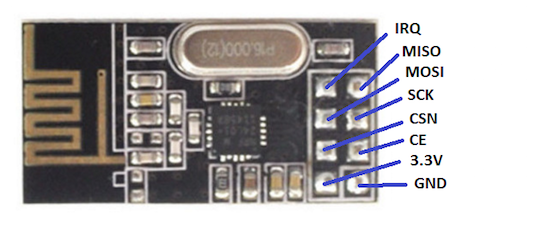
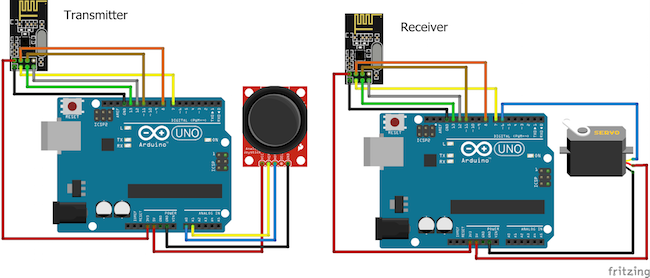
In this project, we are going to control the servo motor using the NRF24L01 and Arduino. We will move the joystick on the transmitter side and, using the NRF24L01, we will send the joystick movement value to the receiver side where we will receive this value and move the servo motor using this value.
Required Components
The components required for this project are as follows:
- 2 Arduino
- 2 NRF24L01 modules
- Joystick module
- Servo motor
- Connecting wires

Required components for this project.
How the Servo Motor Control Works
On the transmitter side we have a joystick module, Arduino, and NRF24L01, while on the receiving side we have an NRF24L01, Arduino, and a servo motor.
When we move the joystick in the horizontal direction, the joystick module will send an analog value to the Arduino. We have set the NRF24L01 module in the transmitter mode, and it will send the joystick movement value at a specific address.
On the receiving side, we have set the NRF24L01 module in the receiving mode. We have given the same address at the receiving side at which the other NRF24L01 module is transmitting the data. So whenever the module will receive the data, the Arduino will read it and will move the servo motor according to it.
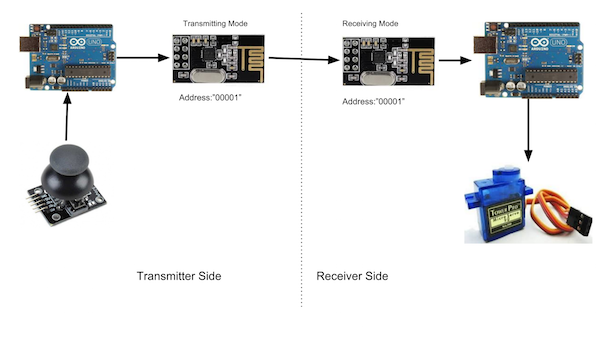
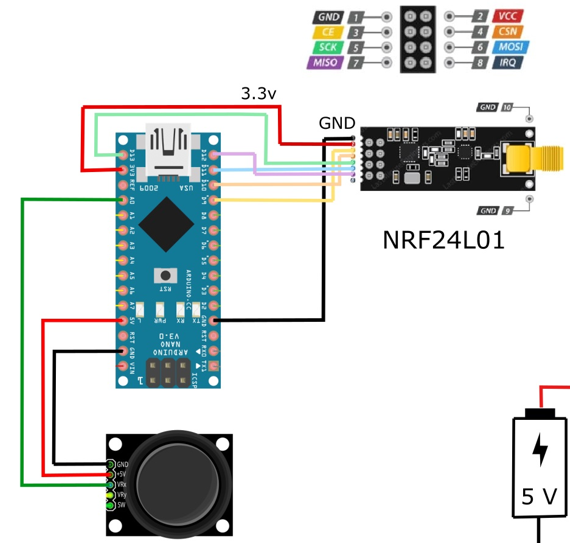
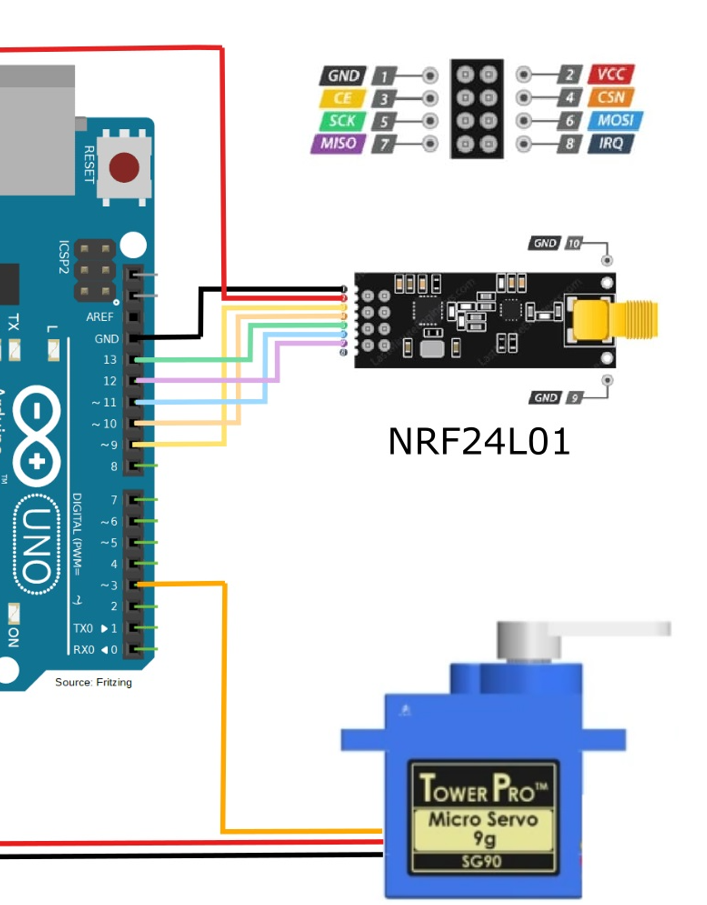
NRF24L01 Pinout
The power consumption of this module is very low. It consumes around 12mA of power during transmission, which is even lower than an LED.
This module operates at 3.3V, so don’t connect it directly to 5V of Arduino, as it can get damaged. The other pins of the NRF24L01 module are 5V tolerant, so you can connect these directly to Arduino.
The SCK, MOSI, and MISO pins are for SPI communication and the CSN and CE pins are for setting the standby or active mode and for setting the transmit or command mode.
Circuit Diagram
The connections are a bit lengthy, so I will explain the connections for transmitter and receiver separately.
For the Transmitter
Make the connections for the transmitter side with the Arduino as follows:
- Connect the 3.3V pin of NRF24L01 with 3.3V of Arduino
- Connect the GND pin of NRF24L01 with GND of Arduino
- Connect the CSN pin of NRF24L01 with pin 8 of Arduino
- Connect the CE pin of NRF24L01 with Pin 7 of Arduino
- Connect the SCK pin of NRF24L01 with pin 13 of Arduino
- Connect the MOSI pin of NRF24L01 with pin 11 of Arduino
- Connect the MISO pin of NRF24L01 with pin 12 of Arduino
Then connect the joystick module with Arduino as follows:
- VCC of joystick module to 5V of Arduino
- GND of joystick module to GND of Arduino
- VER of joystick module to A1 of Arduino
- HOR of joystick module to A0 of Arduino
For the Receiver
On the receiver side, the connections for NRF24L01 with the Arduino are same as those made for the transmitter side. Make the connections for the servo motor with Arduino as follows:
- Red wire to 5V of Arduino
- Brown wire to GND of Arduino
- Yellow wire to Pin 6 of Arduino
Code for the Transmitter
// TX
#include <SPI.h>
#include <RF24.h>
RF24 radio(9, 10); // CE, CSN
const byte direccion[5] = "ITDI";
void setup() {
radio.begin();
Serial.begin(9600);
radio.openWritingPipe(direccion);
radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_MIN);
radio.stopListening();
}
void loop() {
int lecturaADC = analogRead(A0);
int angulo = map(lecturaADC,0, 1023, 0,180);
Serial.println(angulo);
radio.write(&angulo, sizeof(angulo));
delay(50);
}
Code for the Receiver
// RX
#include <SPI.h>
//#include <nRF24L01.h>
#include <RF24.h>
#include <Servo.h>
//pines CE y el CSN
RF24 radio(9,10);
const byte direccion[5] = "ITDI";
Servo myservo;
int angulo =0;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
myservo.attach(3);
radio.begin();
radio.openReadingPipe(0, direccion);
radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_MIN);
radio.startListening();
myservo.write(0);
delay(1000);
myservo.write(180);
delay(1000);
myservo.write(0);
delay(1000);
}
void loop() {
if (radio.available()){
radio.read(&angulo, sizeof(angulo));
Serial.println(angulo);
myservo.write(angulo);
}
}
Project2:
TX.ino
#include<nRF24L01.h>
#include<RF24.h>
#include<SPI.h>
RF24 radio(9, 10);//CE,CSN
const byte address[6] = "ITDI";
int FRONT_LED = A2;
int SERVO = A1;
void setup() {
radio.begin();
radio.openWritingPipe(address);
radio.stopListening();
pinMode(FRONT_LED, INPUT);
pinMode(SERVO, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
int ROBOT[2];
ROBOT[0] = digitalRead(FRONT_LED);
ROBOT[1] = digitalRead(SERVO);
radio.write(&ROBOT,sizeof(ROBOT));
delay(100);
}RX.ino
#include<nRF24L01.h>
#include<RF24.h>
#include<SPI.h>
#include<Servo.h>
Servo myservo;
#define FRONT_LED A2
RF24 radio(9, 10);//CE,CSN
const byte address[6] = "ITDI";
void setup() {
radio.begin();
radio.openReadingPipe(0, address);
radio.startListening();
pinMode(FRONT_LED, OUTPUT);
myservo.attach(3);
}
void loop() {
if(radio.available()){
ROBOT();
}
}
void ROBOT(){
delay(100);
digitalWrite(FRONT_LED, HIGH);
myservo.write(0);
int ROBOT[2];
radio.read(&ROBOT,sizeof(ROBOT));
if(ROBOT[0] == 0){
digitalWrite(FRONT_LED, LOW);
}
if(ROBOT[1] == 0){//SERVO
myservo.write(180);
}
}โค้ดที่ปรับปรุง สำหรับ UNO:
ตัวส่ง (Transmitter)
#include <SPI.h>
#include <nRF24L01.h>
#include <RF24.h>
#define JOYSTICK_X A0 // กำหนดพินสำหรับแกน X ของ Joystick
#define JOYSTICK_Y A1 // กำหนดพินสำหรับแกน Y ของ Joystick
#define BUTTON_1 2 // ปุ่มที่ 1
#define BUTTON_2 3 // ปุ่มที่ 2
RF24 radio(9, 10); // ตั้งค่าพินของ nRF24L01+ (CE, CSN)
struct DataPacket {
int xAxis;
int yAxis;
bool button1;
bool button2;
};
DataPacket data;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
radio.begin();
radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_HIGH); // ตั้งค่า power level
radio.setChannel(0x4c); // ตั้งช่องการสื่อสาร
radio.openWritingPipe(0xF0F0F0F0E1LL); // เปิดการส่งข้อมูลไปยังตัวรับ
radio.setDataRate(RF24_1MBPS); // ตั้งค่าความเร็วในการส่งข้อมูล
pinMode(JOYSTICK_X, INPUT);
pinMode(JOYSTICK_Y, INPUT);
pinMode(BUTTON_1, INPUT_PULLUP);
pinMode(BUTTON_2, INPUT_PULLUP);
}
void loop() {
// อ่านค่าจาก Joystick และปุ่ม
data.xAxis = analogRead(JOYSTICK_X);
data.yAxis = analogRead(JOYSTICK_Y);
data.button1 = digitalRead(BUTTON_1) == LOW;
data.button2 = digitalRead(BUTTON_2) == LOW;
// ส่งข้อมูลไปยังตัวรับ
radio.write(&data, sizeof(data));
delay(100); // หน่วงเวลา 100ms
}ตัวรับ (Receiver)
#include <SPI.h>
#include <nRF24L01.h>
#include <RF24.h>
#define IN1 6
#define IN2 7
#define IN3 8
#define IN4 9
#define ENA 5
#define ENB 4
#define LED_WHITE 10
#define LED_RED 11
RF24 radio(9, 10); // ตั้งค่าพินของ nRF24L01+ (CE, CSN)
struct DataPacket {
int xAxis;
int yAxis;
bool button1;
bool button2;
};
DataPacket data;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
radio.begin();
radio.setPALevel(RF24_PA_HIGH); // ตั้งค่า power level
radio.setChannel(0x4c); // ตั้งช่องการสื่อสาร
radio.openReadingPipe(1, 0xF0F0F0F0E1LL); // เปิดการรับข้อมูลจากตัวส่ง
radio.setDataRate(RF24_1MBPS); // ตั้งค่าความเร็วในการส่งข้อมูล
radio.startListening(); // เริ่มรับข้อมูล
// กำหนดพินที่ใช้
pinMode(IN1, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN2, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN3, OUTPUT);
pinMode(IN4, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENA, OUTPUT);
pinMode(ENB, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED_WHITE, OUTPUT);
pinMode(LED_RED, OUTPUT);
stopMotors(); // เริ่มต้นมอเตอร์ให้หยุด
}
void loop() {
if (radio.available()) {
radio.read(&data, sizeof(data)); // อ่านข้อมูลที่ส่งมาจากตัวส่ง
// ควบคุมทิศทางการเคลื่อนที่ของมอเตอร์
if (data.yAxis < 400) { // ถอยหลัง
backward(255);
} else if (data.yAxis > 600) { // เดินหน้า
forward(255);
} else if (data.xAxis < 400) { // เลี้ยวซ้าย
turnLeft(255, 128);
} else if (data.xAxis > 600) { // เลี้ยวขวา
turnRight(128, 255);
} else {
stopMotors(); // หยุดมอเตอร์
}
// เปิดไฟ LED ตามปุ่ม
if (data.button1) {
digitalWrite(LED_WHITE, HIGH); // เปิดไฟสีขาว
digitalWrite(LED_RED, LOW); // ปิดไฟสีแดง
} else if (data.button2) {
digitalWrite(LED_RED, HIGH); // เปิดไฟสีแดง
digitalWrite(LED_WHITE, LOW); // ปิดไฟสีขาว
} else {
digitalWrite(LED_WHITE, LOW); // ปิดไฟสีขาว
digitalWrite(LED_RED, LOW); // ปิดไฟสีแดง
}
}
}
// ฟังก์ชันเดินหน้า
void forward(int speed) {
digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN4, LOW);
analogWrite(ENA, speed);
analogWrite(ENB, speed);
}
// ฟังก์ชันถอยหลัง
void backward(int speed) {
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN2, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN3, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4, HIGH);
analogWrite(ENA, speed);
analogWrite(ENB, speed);
}
// ฟังก์ชันเลี้ยวขวา
void turnRight(int speedLeft, int speedRight) {
digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4, HIGH);
analogWrite(ENA, speedLeft);
analogWrite(ENB, speedRight);
}
// ฟังก์ชันเลี้ยวซ้าย
void turnLeft(int speedLeft, int speedRight) {
digitalWrite(IN1, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3, HIGH);
digitalWrite(IN4, LOW);
analogWrite(ENA, speedLeft);
analogWrite(ENB, speedRight);
}
// ฟังก์ชันหยุดมอเตอร์
void stopMotors() {
digitalWrite(IN1, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN2, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN3, LOW);
digitalWrite(IN4, LOW);
analogWrite(ENA, 0);
analogWrite(ENB, 0);
}Link:https://maker.pro/arduino/projects/how-to-control-a-servo-motor-using-arduino-a-joystick-module-and-nrf24lo1